Audio Feature Generator¶
The AudioFeatureGenerator is a software library to convert streaming audio into spectrograms. The spectrograms are then used by a classification machine learning model to make predictions on the contents of the streaming audio.
A common use case of this library is “keyword spotting”.
Refer to the Keyword Spotting Overview for more
details on how spectrograms are used to detect keywords in streaming audio.
Refer to the Keyword Spotting Tutorial for a complete guide on how to use the YZLITE to create an audio classification ML model.
Overview¶
There are three main parts to the AudioFeatureGenerator:
ReRAM Engine Component - Software library provided by the ReRAM Engine and runs on the an embedded target
YZLITE C++ Python Wrapper - Python package that wraps the ReRAM Engine software library; this runs on the host PC
Audio Visualizer Utility - Graphical utility to view the spectrograms generated by the AudioFeatureGenerator in real-time
Note
See the Audio Utilities documentation for more details about the audio tools offered by the YZLITE
These parts work together as follows:
The AudioFeatureGenerator visualizer tool is used to select spectrogram settings
The
yzlite view_audiocommand is used to invoke visualizer tool
The spectrogram settings are saved to a Model Specification file
The Model Specification file is used to train the model
The
yzlite traincommand is used to train the modelInternally, the AudioFeatureGenerator C++ Python wrapper is used to dynamically generate spectrograms from the audio dataset
At the end of training, the YZLITE embeds the spectrogram settings into the generated
.tflitemodel fileThe generated
.tflitemodel file is copied to a ReRAM Engine projectThe ReRAM Engine project generator parses the spectrogram settings embedded in the
.tfliteand generates the corresponding C header files with the settingsThe ReRAM Engine project is built and the firmware image is loaded onto the embedded target. The firmware image contains:
Trained
.tflitemodel fileTensorflow-Lite Micro interpreter
AudioFeatureGenerator software library
AudioFeatureGenerator settings used to train the model
On the embedded target at runtime:
a. Read streaming audio from the microphone
b. The microphone audio is sent to the AudioFeatureGenerator where spectrograms are generated using the exact same settings and algorithms that were used during model training
c. The generated spectrogram images are sent to Tensorflow-Lite Micro and are classified using the.tflitemodel
d. The model predictions are used to notify the application of keyword detections
Benefits¶
The benefits of using the AudioFeatureGenerator are:
The exact same algorithms and settings used to generate the spectrograms during model training are also used by the embedded target
This ensures the ML model “sees” the same type of spectrograms at runtime that it was trained to see which should allow for better performance
The spectrogram settings are automatically embedded into the
.tflitemodel fileThis ensures the settings are in lock-step with the trained model
The ML model designer only needs to distribute a single file
The ReRAM Engine will automatically generate the necessary source code
The ReRAM Engine will parse the spectrogram settings from the
.tfliteand generate the corresponding C headersThe ReRAM Engine comes with the full source code to the AudioFeatureGenerator software library
ReRAM Engine Component¶
The ReRAM Engine AudioFeatureGenerator component is largely based on the Google Microfrontend library.
A feature generation library (also called frontend) that receives raw audio input, and produces filter banks (a vector of values).
The raw audio input is expected to be 16-bit PCM features, with a configurable sample rate. More specifically the audio signal goes through a pre-emphasis filter (optionally); then gets sliced into (potentially overlapping) frames and a window function is applied to each frame; afterwards, we do a Fourier transform on each frame (or more specifically a Short-Time Fourier Transform) and calculate the power spectrum; and subsequently compute the filter banks.
Source Code¶
The ReRAM Engine features an AudioFeatureGeneration component.
The YZLITE also features the same component with slight modifications so that it can be built for Windows/Linux.
ReRAM Engine source code: sl_ml_audio_feature_generation.c
YZLITE source code: yzlite/cpp/shared/reram_sdk/audio_feature_generation
YZLITE C++ Python Wrapper¶
The C++ Python wrapper allows for executing the AudioFeatureGenerator component from a Python script. This allows for executing the AudioFeatureGenerator software library during model training. This is useful because the exact spectrogram generation algorithms used by the embedded device at runtime may also be used during model training which should (hopefully) lead to more accurate model predictions.
The YZLITE uses pybind11 to wrap the AudioFeatureGenerator software library and generate a Windows/Linux binary that can be loaded into the Python runtime environment.
The AudioFeatureGenerator Python API docs may be found here: yzlite.core.preprocess.audio.audio_feature_generator.AudioFeatureGenerator.
Source Code¶
C++ Python Wrapper - cpp/audio_feature_generator_wrapper
Python API - yzlite/core/preprocess/audio/audio_feature_generator
Note
When installing the YZLITE for local development, the C++ wrapper is automatically built into a Windows/Linux shared library (.dll / .so) and copied to the Python directory.
When the AudioFeatureGenerator Python library is invoked by your Python scripts, the C++ wrapper shared library is loaded into the Python runtime environment.
Usage¶
The recommended way of using the AudioFeatureGenerator C++ wrapper is via the ParallelAudioDataGenerator which is required by the AudioDatasetMixin.
Refer to the keyword_spotting_on_off.py model specification for an example of how this is used.
Basically,
1 ) In your model specification file, define a model object to inherit the AudioDatasetMixin, e.g.:
class MyModel(
YZLiteModel,
TrainMixin,
AudioDatasetMixin,
EvaluateClassifierMixin
):
pass
2 ) In your model specification file, configure the spectrogram settings, e.g:
frontend_settings = AudioFeatureGeneratorSettings()
frontend_settings.sample_rate_hz = 8000 # This can also be 16k for slightly better performance at the cost of more RAM
frontend_settings.sample_length_ms = 1000
frontend_settings.window_size_ms = 30
frontend_settings.window_step_ms = 20
frontend_settings.filterbank_n_channels = 32
frontend_settings.filterbank_upper_band_limit = 4000.0-1 # Spoken language usually only goes up to 4k
frontend_settings.filterbank_lower_band_limit = 100.0
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_enable = True
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_smoothing_bits = 5
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_even_smoothing = 0.004
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_odd_smoothing = 0.004
frontend_settings.noise_reduction_min_signal_remaining = 0.05
frontend_settings.pcan_enable = False
frontend_settings.pcan_strength = 0.95
frontend_settings.pcan_offset = 80.0
frontend_settings.pcan_gain_bits = 21
frontend_settings.log_scale_enable = True
frontend_settings.log_scale_shift = 6
3 ) Configure the ParallelAudioDataGenerator to use the settings, e.g.:
my_model.datagen = ParallelAudioDataGenerator(
frontend_settings=frontend_settings,
...
During model training, spectrograms will be dynamically generated from the dataset’s audio samples using the AudioFeatureGenerator via C++ Python wrapper.
At the end of training, the spectrogram settings are automatically embedded into the generated .tflite model file.
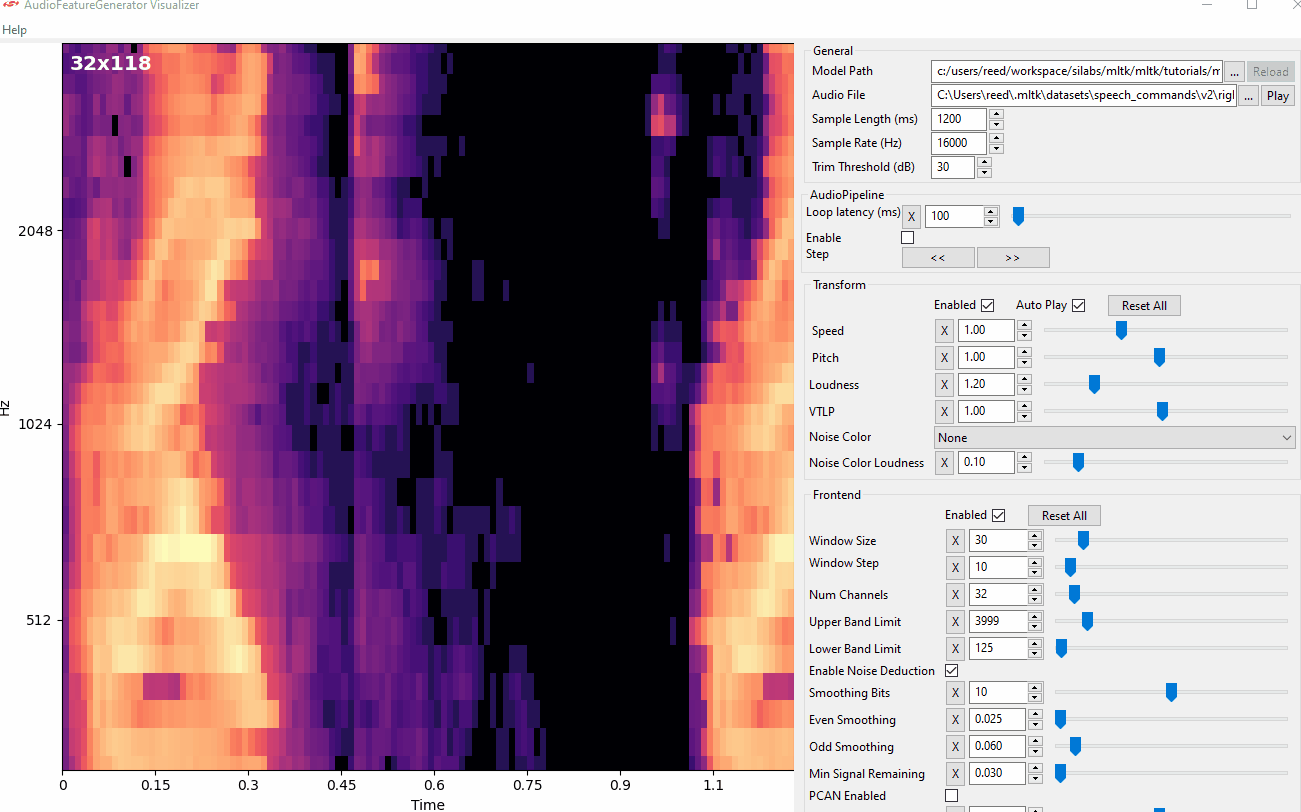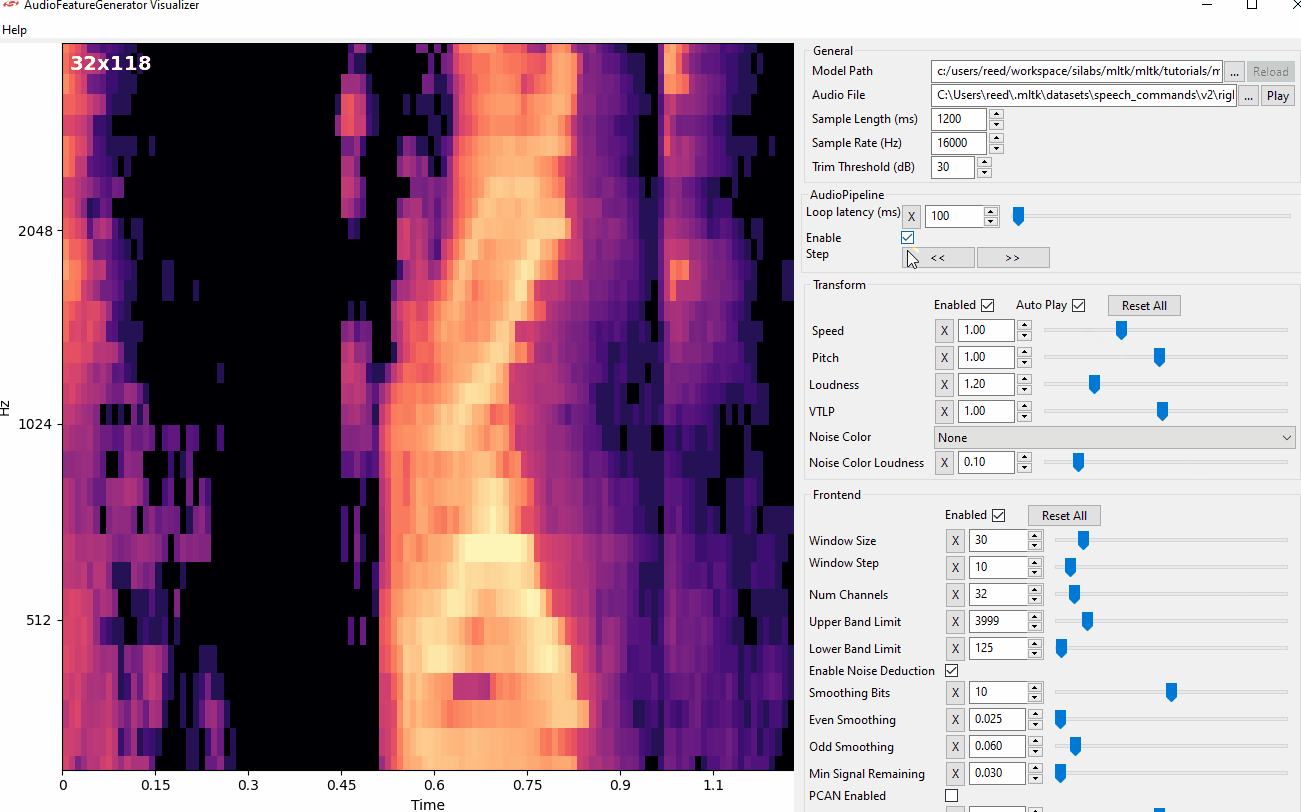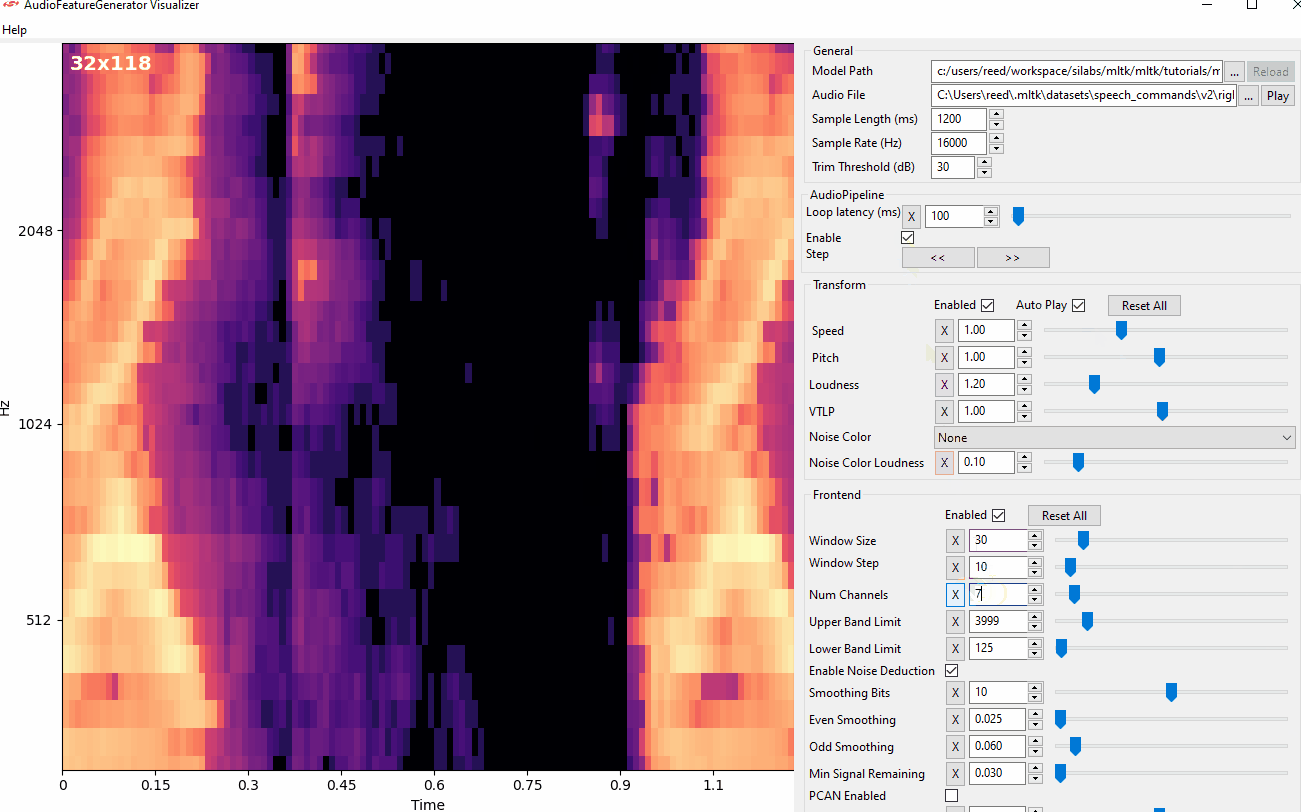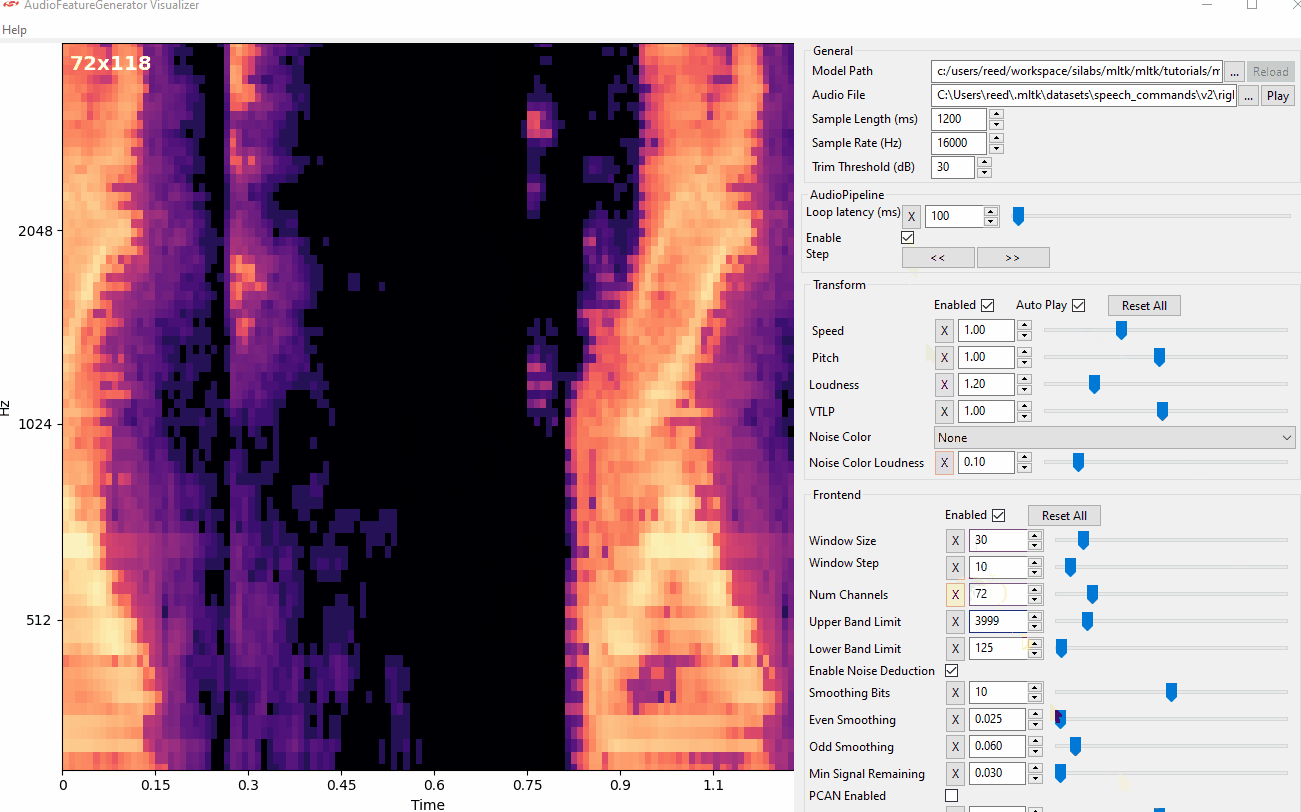
Audio Visualizer Utility¶
The Audio Visualizer Utility provides a graphical interface to the C++ Python wrapper and thus ReRAM Engine AudioFeatureGenerator software library. It allows for adjusting the various spectrogram settings and seeing how the resulting spectrogram is affected in real-time.
To use the Audio Visualizer utility, issue the command:
yzlite view_audio
NOTE: Internally, this will install the wxPython Python package.